What Causes Acne?
What is acne?
Acne primarily develops in adolescents during puberty. Androgens (male sex hormones) are the primary determinant of acne along with the presence of the bacteria P. acnes, and fatty acids (sebum) present in oil (sebaceous) glands.
Acne mainly appears on your face, chest, shoulders, and back. Diets with a high glycemic index or dairy can worsen acne.
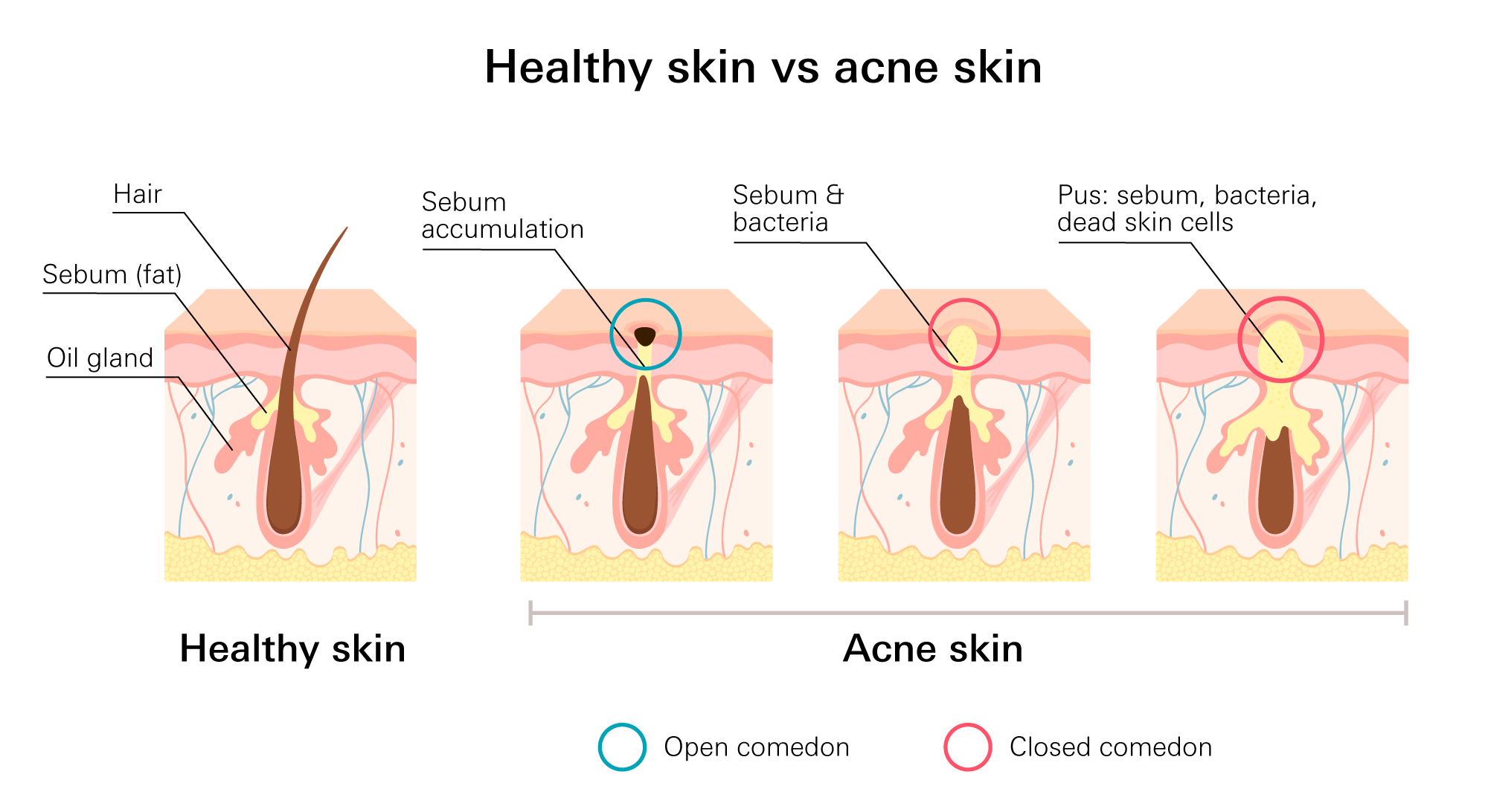
Types of acne
Acne often develops as a result of clogged skin pores. Too much oil, bacteria, or skin cell formation, as well as hormonal changes, can all lead to clogged pores.
Acne lesions can be classified into several types, including whiteheads, blackheads, small bumps, cysts, and nodules.
- Noninflammatory acne—includes blackheads and whiteheads. These types of acne don’t generally result in swelling.
- Inflammatory acne—including papules, pustules, cysts, and nodules, are pimples that are red and swollen.
Inflammatory acne is mostly caused by sebum (fat) and dead skin cells, but bacteria can also contribute to pore-clogging (comedones). Deep within your skin’s surface, bacteria can infect it and result in an infection. This could lead to excruciating acne lesions that are challenging to remove.
- Whiteheads (closed comedones/plugged pores)
—Whiteheads are pores that are kept closed by dead skin cells and oil/ sebum.
—Because the pores are already closed, treating whiteheads is more challenging.
- Blackheads (open comedones/plugged pores)
—Blackheads are open pores on your skin that collect excess oil and dead skin. Even though the rest of the pore is blocked, the top remains open.
—The black patches, which mimic dirt deposits, are produced by an uneven light reflection off the clogged follicle.

- Papules
—Papules are inflamed, tiny pimples that are red or pink.
—As a result, the pores become tender to the touch and become hard and clogged.

- Pustules
—Pustules are pimples that have pus (unlike papules).
—These bumps protrude from your skin and are typically red. On top, they frequently feature yellow or white heads.
—If this type of acne is picked or scratched, it may cause scarring.
- Nodules
—Nodules are clogged, deep, swollen pores on your skin.
—This type of acne tends to be large and painful.
—Nodules, as opposed to pustules and papules, are located deeper underneath your skin.
—Nodules are often difficult to treat at home because they are located so deeply within the skin. To help with this, prescription medication is recommended.
- Cysts
—Cysts are pimples with pus. This type of acne may leave scars.
—Cysts can form when bacteria, sebum, and dead skin cells combine and clog your pores. More below the surface than nodules, the blockages develop deep within your skin.
—These big, red or white, bumps are frequently uncomfortable to touch and very painful. The largest type of acne, cysts, are typically formed as a result of a severe infection.
What causes acne?
There are 4 leading causes of acne:
- Bacteria (P. acnes)
- Inflammation
- Excess oil (sebum) production
- Hair follicles clogged by oil and dead skin cells
Acne develops when the male hormones produced by the adrenal glands in both males and females during puberty cause the oil (sebaceous) glands to become active.
Oil is a lubricating and protective natural substance for your skin. In some cases, cells that are near to the surface obstruct sebaceous gland openings, resulting in an accumulation of oil underneath. Everybody's skin has bacteria that are stimulated by this oil. The bacteria generally cause no problems, but when stimulated, they proliferate. As a result, the surrounding tissues become inflamed.
Other factors that could cause acne:
- Hormonal changes
Both boys and girls have androgens, which are hormones that surge during puberty and induce the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce more sebum. Breakouts can also result from hormonal changes around midlife, particularly in women. - Certain medications
Examples include medications containing corticosteroids, testosterone, or lithium. Some oral contraceptive pills help relieve acne, but some may make acne worse. - Stress
Although stress doesn't directly cause acne, evidence indicates that it can worsen acne in individuals who are already prone to breakouts by causing hormonal changes. - Diet
According to studies, eating certain foods, such as carbohydrate-rich foods, for example, bread, bagels, and chips may worsen your acne. If you regularly consume foods and beverages like soda, white bread, white rice, and cake, you're more prone to develop acne. - Cosmetics
The majority of cosmetics and skin care items don't clog pores (comedogenic.) Better options include those that are "water-based" or "oil-free" (non-comedogenic). - Heredity
There is no particular gene for acne. However, whether you are prone to acne may depend on your genetics.
What are treatment options for acne?
Acne is treated by these primary groups of agents:
Benzoyl peroxide (BPO)
BPO is the most effective over-the-counter (OTC) agent that is sold in gels, lotions, and cleansers. It’s also available by prescription, including in combination with the retinoid adapalene.
Dead skin cells and bacteria that block your pores can be successfully removed by BPO. It clears clogged pores, dries up zits, eradicates bacteria underneath your skin, as well as prevents new acne. BPO is effective for inflammatory acne, such as pustules, papules, cysts, and nodules.
Benzoyl peroxide can cause a rare but serious allergic reaction or severe skin irritation. Stop using this medicine and get emergency medical help if you have: hives, itching; difficulty breathing, feeling light-headed; or swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid may not only help with acne treatment but also exfoliates dead skin cells from within the follicle, aiding in the maintenance of clear pores. Salicylic acid also aids in reducing inflammation and oil production. Blackheads and non-inflamed breakouts respond best to it.
It is a mildly useful OTC agent and is primarily used in “medicated pads” for facial cleansing. Skin darkening and slight skin irritation are among the side effects.
Avoid using salicylic acid scrubs or other skin products that can cause dryness or irritation, such as harsh soaps, shampoos, skin cleansers, hair removers or waxes, or skin products with alcohol, or spices, astringents, or lime, while starting a retinoid; this will worsen irritation.
Retinoids
Retinoids, primarily topical tretinoin and derivatives are the prescription medications of choice for acne and are also used to reduce wrinkles and hyperpigmentation (dark spots on your skin).
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved topical retinoids for the treatment of whiteheads, blackheads, and acne lesions. Topical retinoids remove your dead skin cells and increase the production of new skin cells. Additionally, retinoids have anti-inflammatory properties.
Learn more about prescription retinoid options.