- Cold sores are fluid-filled blisters on or around the lips, caused by the HSV-1 virus.
- The virus stays in your body for life and can reactivate due to triggers like stress, illness, or sun exposure.
- Symptoms often start with tingling or itching, followed by blisters that scab and heal over 7–10 days.
- Cold sores are highly contagious from the first tingle until fully healed.
- Treatment includes over-the-counter creams and prescription antivirals to reduce symptoms and speed healing.
Overview
Cold sores are small, fluid-filled blisters that typically appear on or around the lips. They often begin with a tingling, itching, or burning sensation before a blister forms, breaks open, and eventually scabs over as it heals. This process usually takes about a week or longer.
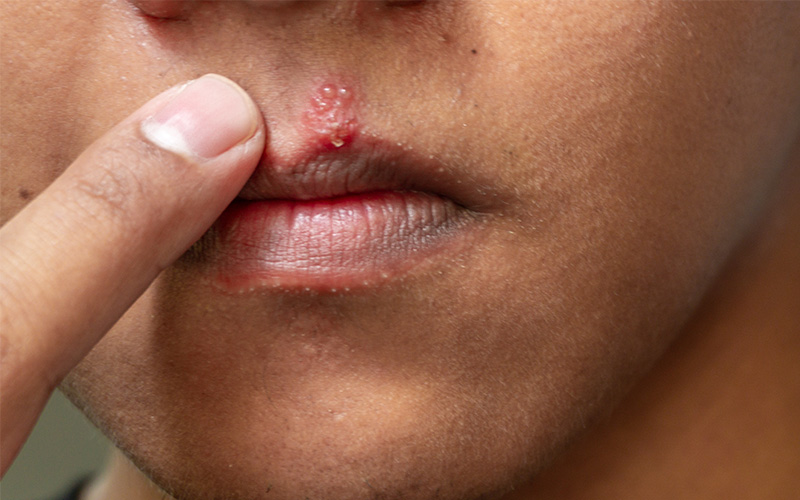
These sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), which remains in the body for life. While some people never show symptoms, others experience recurring outbreaks triggered by stress, illness, fatigue, or sun exposure.
Cold sores are highly contagious and can spread through direct contact, such as kissing, or by sharing items like utensils or lip balm. The virus can also spread to other parts of the body if proper hygiene isn’t followed.
Most people are exposed to HSV-1 in childhood, often without noticeable symptoms. Though HSV-1 is the main cause of cold sores, it can also cause genital infections. Similarly, HSV-2 typically linked to genital herpes can occasionally cause cold sores.
Prevalence
THerpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is extremely common in the United States. Most people are exposed during childhood through everyday interactions, such as sharing utensils, drinks, or receiving a kiss from a family member.
By adulthood, over half of Americans have been infected, with some estimates ranging from 70% to 80%. However, not everyone who carries the virus develops cold sores. Some may never experience symptoms, while others may go years between outbreaks.
Although HSV-1 is widespread, visible symptoms vary greatly from person to person.
Symptoms
Cold sores often begin with early warning signs before anything appears on the skin. These may include:
- Tingling, itching, or burning near the lips
- Redness or tenderness in a specific spot
- A tight or uncomfortable feeling, especially when eating or talking
- Mild swelling or irritation
During a first outbreak, additional symptoms may occur, such as:
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Sore throat or headache
Symptoms vary widely. Some people experience only mild irritation, while others may have more noticeable discomfort.
Cold Sore Stages
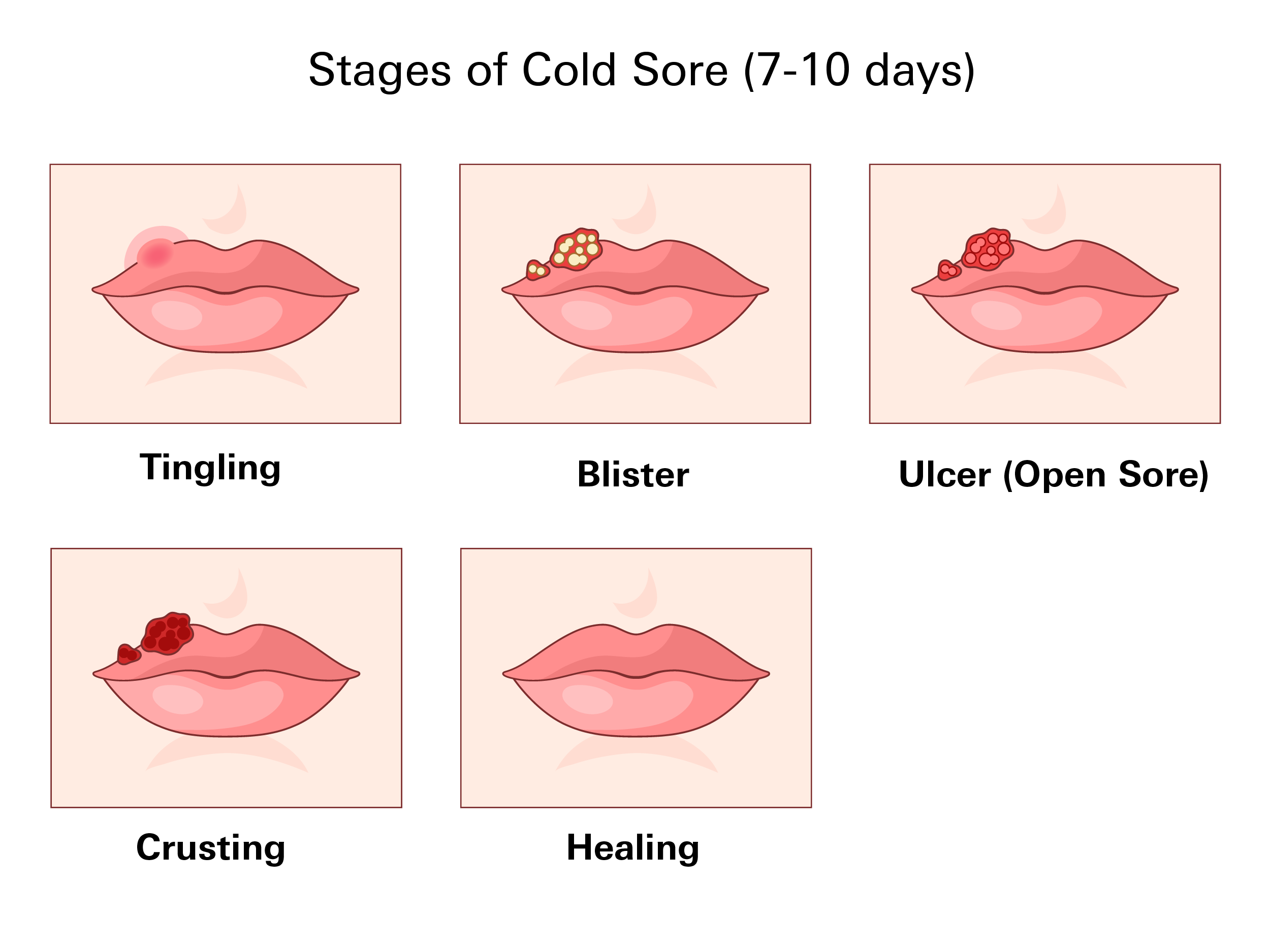
Cold sores typically progress through five stages over 7 to 10 days:
- Tingling: A tingling, itching, or burning sensation signals the start of an outbreak. The virus is active and contagious, even before a blister appears.
- Blister: Small, fluid-filled blisters form, often in clusters. The area may be red and swollen. This is one of the most contagious stages.
- Ulcer (Open Sore): Blisters break open, forming a shallow, painful sore. This stage is moist and highly contagious.
- Crusting (Scabbing): A scab forms as the sore begins to dry. Cracking and flaking may occur. While less contagious, the virus can still spread if the scab is disturbed.
- Healing: The scab falls off, and the skin heals. Mild redness or sensitivity may remain, but the area is no longer contagious once fully closed.
Cold sores are contagious from the first sign of tingling until the skin is completely healed. This period usually lasts 7 to 10 days but can be longer if healing is delayed or the sore is reopened.
Causes
Cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Once the virus enters the body, it remains there for life, hiding in nerve cells and often staying inactive for long periods. You may not experience symptoms for months or even years, but the virus is still present even when inactive.
Outbreaks occur when the dormant virus becomes active again, not from a new infection. Common triggers include:
- Illness, especially colds or fevers
- Emotional or mental stress
- Lack of sleep
- Excessive sun exposure
- Hormonal changes, such as during menstruation
- Dental procedures or mouth irritation
- A weakened immune system due to illness or medications
Some people have consistent triggers, while others may experience outbreaks unpredictably. In some cases, cold sores appear without any clear cause.
Risk Factors
HSV-1 spreads easily through everyday contact. Certain behaviors and conditions can increase your risk of becoming infected.
You may be at higher risk if you:
- Have close contact with someone who carries the virus
- Share items like utensils, drinks, towels, or lip balm
- Kiss someone with an active cold sore or during viral shedding
- Engage in oral-genital contact with a partner who has HSV-1
- Live or work in crowded or communal environments
- Have a weakened immune system
Diagnosis
Most cold sores can be diagnosed based on their appearance, location, and symptoms. A healthcare provider can usually confirm HSV-1 without any tests.
In certain cases such as severe, recurring, or unusually located sores, a swab may be taken from the blister to test for the virus. Blood tests can also detect past exposure to HSV-1, but they are rarely needed for routine diagnosis.
Treatment
Cold sores can be painful and unpredictable, but several treatments can help reduce discomfort and speed up healing. These include over-the-counter (OTC) remedies and prescription antiviral medications.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
- Docosanol (Abreva): A topical antiviral cream that helps prevent HSV-1 from entering healthy skin cells, reducing the duration and severity of symptoms when applied early.
- Campho-phenique: A topical solution containing camphor and phenol, used to relieve discomfort and dry out blisters.
- Orajel Touch-Free: Contains benzocaine (a topical anesthetic) or benzalkonium chloride (an antiseptic). It numbs the sore for pain relief but does not treat the virus. Some versions have a no-contact applicator to reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
- Herpecin-L Everyday Protection: A daily-use lip balm that may help cold sores heal faster and reduce their frequency. It contains SPF 30, lysine, lemon balm, and vitamins C, B6, and E to protect and soothe lips.
Prescription Antiviral Medications
- Valacyclovir (Valtrex): An oral tablet approved for patients 12 and older. It blocks viral replication, shortens outbreaks, and reduces severity. Best taken at the first sign of symptoms
- Acyclovir (Zovirax): Available as a topical cream or buccal tablet. It inhibits viral DNA polymerase, preventing the virus from multiplying.
- Famciclovir: An oral tablet (not approved for those under 18) that is converted to penciclovir in the body to stop viral replication.
- Penciclovir (Denavir): A topical antiviral cream for patients 12 and older, used for recurrent outbreaks. ay be used during pregnancy if advised by a healthcare provider.
Prevention
While there’s no cure for HSV-1, you can reduce the risk of outbreaks and transmission by managing triggers and practicing good hygiene.
To Prevent Outbreaks
- Avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially on the lips
- Use lip balm with SPF daily
- Manage stress through rest, exercise, and relaxation
- Get adequate sleep
- Support your immune system with a healthy lifestyle
- Consider daily antiviral medication if prescribed for frequent outbreaks
To Prevent Spreading HSV-1
- Avoid kissing or sharing drinks, utensils, or lip products during an outbreak
- Refrain from oral-genital contact when symptoms are active
- Wash hands after touching your face
- Avoid touching the sore, especially if you have eczema, wear contact lenses, or have broken skin
- Do not pick at or peel the sore while it’s healing
Related Topics
Valacyclovir: A Medication to Treat Cold Sores and Shingles
Valacyclovir, commonly known by its brand name Valtrex, is an antiviral medication that helps manage infections caused by specific types of viruses. It is used to treat several viral infections, with treatment guidelines varying between adults and children.
Read moreFight Cold Sores with Acyclovir
Acyclovir cream is a topical medication used to treat cold sores. It is one of several treatment options for cold sores, which also include oral medications.
Read moreCold Sores: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Cold sores, also commonly referred to as herpes labialis, are small, painful, fluid-filled blisters or sores. These typically appear on or around the lips. They can also occur on the face or inside the mouth.
Read more