Opill: The First OTC Birth Control Pill in the U.S.
- Opill is the first FDA-approved birth control pill available in the U.S. without a prescription since July 2023.
- Opill is a progestin-only pill, meaning it does not contain estrogen, and works by preventing ovulation and thickening cervical mucus.
- Opill is up to 98% effective with perfect use but less effective if doses are missed.
- Common side effects include irregular periods, headache, and nausea.
- Opill does not protect against sexually transmitted infections or HIV.
In July 2023, the FDA approved Opill, making it the first birth control pill available without a prescription in the U.S.
You can now purchase Opill directly from a pharmacy. This eliminates the need for a doctor's visit or a prescription. This change removes barriers for many women, especially those without easy access to a doctor or health insurance.
What Is Opill?
Opill is a progestin-only birth control pill. It contains norgestrel and does not include estrogen. This difference can be important for some users.
- Not emergency contraception: Opill is not a morning-after pill.
- Not an abortion pill: It prevents pregnancy but does not end it.
- Daily use: Take one pill at the same time every day.
How to Take It
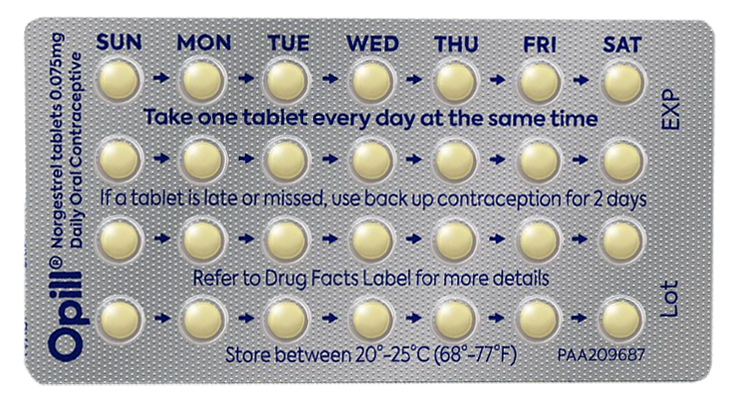
- Start on any day of your cycle.
- Take 1 pill daily, at the same time each day.
- There are no breaks between packs. Start a new pack the day after finishing the last one.
- Opill becomes effective 48 hours after your first dose. Use backup protection (like condoms) for the first 2 days.
- Opill has no age restrictions. Anyone who has started menstruating can use it.
Effectiveness
Opill is up to 98% effective with perfect use (taking it consistently and on time). However, missing a dose, taking it at the wrong time, or not using backup protection when needed can reduce its effectiveness.
What to Do If You Miss a Dose
To maintain maximum protection, take Opill at the same time every day. Follow these steps if you miss a dose:
- Less than 3 hours late: Take the missed pill as soon as you remember. Continue your regular schedule.
- More than 3 hours late or missed more than one pill:
- Take one pill as soon as you remember.
- Take the next pill at your usual time (you may take two pills in one day).
- Use backup protection for the next 2 days.
- Vomiting or severe diarrhea within 4 hours of taking a pill:
- Do not take another pill.
- Continue with your next scheduled dose.
- Use backup protection for the next 2 days.
How Opill Works
Opill is a progestin-only birth control pill. It prevents pregnancy in several ways:
- Ovulation Suppression: Opill stops ovulation in about half of menstrual cycles.
- Thickens Cervical Mucus: This makes it harder for sperm to move through the cervix and reach an egg.
- Lowers hormone levels: It reduces the mid-cycle peaks of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which are involved in ovulation.
- Slows egg movement: It slows the egg’s travel through the fallopian tubes.
- Alters the uterine lining: It changes the endometrium, making it less likely for a fertilized egg to implant.
Safety Profile
Most people can take Opill safely, but it may not be suitable for everyone. Consider the following before starting Opill.
Common Side Effects
- Irregular periods or changes in bleeding
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Increased appetite
- Stomach cramps or pain
- Bloating
- Fatigue
- Vaginal discharge
- Nervousness
- Backache
- Breast tenderness
- Acne
Serious Side Effects (Rare)
If you experience any of the following, stop taking Opill and seek immediate medical attention:
- Signs of ectopic pregnancy: lower abdominal pain, spotting
- Liver problems: yellowing of the skin or eyes, stomach pain, dark urine, pale stools, fever, fatigue, or loss of appetite
- Mood changes or depression
- Increased risk of breast or cervical cancer with long-term use
Menstrual Changes
Some people may stop having periods while taking Opill. In studies, about 3 out of 10 users did not get a period, sometimes as early as the first cycle. If you miss two periods in a row, or your period is late and you missed a pill, take a pregnancy test.
Talk to Your Healthcare Provider
Speak with your healthcare provider before using Opill if you have ever had:
- Breast cancer
- Liver problems
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding
Drug Interactions
Certain medications can make Opill less effective. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you take:
- Seizure medications (phenytoin, carbamazepine, barbiturates)
- Tuberculosis treatments (rifampin)
- HIV medications (efavirenz)
- Drugs for pulmonary hypertension (bosentan)
- St. John’s wort (a herbal supplement for mood)
If you use any of these, talk to a healthcare provider before starting Opill. These drugs can lower hormone levels, making Opill less reliable.
If you have recently taken ulipristal acetate (emergency contraception, brand name Ella), wait five full days before starting Opill. Use condoms or another barrier method until your next period after starting Opill.
Opill does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or HIV. This includes infections like chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
Buying Opill
Opill is available over the counter, which means you can find it in most pharmacies, some grocery stores, and online without a prescription.
You can also order it directly from our website at Marley Drug Pharmacy. If you have any questions or need help figuring out if Opill is right for you, feel free to call and speak with one of our pharmacists. We’re here to help.